DHCP Penetration Testing
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and a DHCP server dynamically assigns an IP address to enable hosts (DHCP Clients). Basically DHCP server reduce the manually effort of administer of configuring IP address in client machine by assign a valid IP automatically to each network devices. A DHCP is available for distributing IP address of any Class among: A B C D E basis on their netmask description which means it is applicable even for small network or a huge network.
DHCP uses UDP as its transport protocol. The client sends messages to the server on port 67 and the server sends messages to the client on port 68.
There are three mechanisms used to assign an IP address to the client. They are:
- Automatic allocation – DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a client
- Manual allocation – Client’s IP address is assigned by the administrator, DHCP conveys the address to the client.
- Dynamic allocation– DHCP assigns an IP address to the client for a limited period of time (lease).
Mode of Operation DHCP server and DHCP Client
- DHCP Discover: DHCP client broadcast a DHCP discover message to DHCP server for an IP address lease request through subnet mask for e.g. 255.255.255.255.
- DHCP Offer: DHCP server receives DHCP Discover message for an IP address lease form DHCP client and reserve IP for it and send DHCP OFFER message to DHCP Client for IP lease.
- DHCP Request: DHCP client broadcast a message to DHCP server for acceptance of IP by receiving Offered IP packets and make DHCP request for IP parameter configuration.
- DHCP Acknowledgment: DHCP server receives DHCP client request for IP configuration process and as responds DHCPACK message sent to client with committed IP address and its configuration and with some additional information such lease time of offered IP.
- DHCP Release: DHCP client sends a DHCP Release packet to the DHCP server to release the IP address.

DHCP Starvation Attack
A DHCP starvation attack may also categories as DHCP DOS attack where the attacker broadcasting fake DHCP requests with spoofed MAC addresses. If official replies to this fake request then it can exhaust the address space available to the DHCP servers for a period of time. This can be performed by using attacking tools such as “Yersinia”.
Now attacker may place rouge server in the network and respond to new DHCP requests from clients.
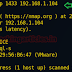
Form given below image you can observe that by executing given command we discovered bind hardware with our official router. Here we had used CISCO router for DHCP penetration testing.
ip dhcp binding

Launch DHCP Starvation Attack using Yersinia
Yersinia is a network tool designed to take advantage of some weakness in different network protocols. It pretends to be a solid framework for analyzing and testing the deployed networks and systems.
Currently yersinia supports:
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP)
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
IEEE 802.1Q
IEEE 802.1X
Inter-Switch Link Protocol (ISL)
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
From http://www.yersinia.net/
By default in Kali Linux installed yersinia is available for DHcp penetration testing, open the terminal and execute given command which will open yersinia in GUI mode as shown in given below image.
yersinia -G

You will observe few tabs in menu bar click on launch attack; a small window will pop up for choosing protocol for attack here we had select DHCP, now enable the option for sending DISCOVER packet.

Now it will start sending Discovered packet to the router for release IP for each of its fake Discover message as shown in given image.

From given below image you can observe wireshark has capture the DHCP packet where the attacker machine as source 0.0.0.0 is broadcasting DISCOVER message to Destination on 255.255.255.255. This is DHCP starvation attack which also considered as DHCP Dos attack because its send Discover message infinitely in network to block the responded server for other genuine request from other DHCP client.

Now when again you will check our router IP table then you will observe that all IP is allocated on some different-different Hardware address as shown in given below image.

Rogue DHCP Server
A rough DHCP server is a forged server of attacker which is place in a local network for stealing information that is being shared among several clients. After DHCP starvation attack, the official DHCP server is unable to Offer IP to DHCP client. Therefore when a client release its old IP and request new IP by broadcasting DHCP Discover message then rough server offer an IP as responds to the DHCP client and hence Client request for IP configuration from fake server and get trap into fake network. Now if client is transferring any information over fake network that can easily sniff by rough server.

Form given below image you check attacker’s machine IP is 192.168.1.104 which will reflect as DNS address in victim’s machine (Windows’s).

Now open the terminal and type “msfconsole” for metasploit framework and execute given below commands which will create your Rouge server in the network.
use auxiliary/server/dhcp
msf auxiliary(dhcp) > set srvhost 192.168.104
msf auxiliary(dhcp) >set netmask 255.255.255.0
msf auxiliary(dhcp) >set DHCPIPSTART 192.168.1.200
msf auxiliary(dhcp) >set DHCPIPEND 192.168.1.205
msf auxiliary(dhcp) >Exploit
If you perceive above command then you will find that it will Start DHCP service and behave like a DHCP server which will offer Class C IP to official DHCP client form specified pool between 192.168.1.200 to 192.168.1.205.
Now turn on any another system in network and check its IP configuration.

Let’s study the given image where attack is broadcasting Offer packet in the network and then in 2nd packet we saw DHCP ACK which means some DHCP client ask for offered IP configuration then we can see DNS query send from an IP 192.168.1.202 to 192.168.1.104.

Form given below image you can observed that 192.168.1.202 IP is allocated to ubuntu which is official DHCP client. Now if client is transferring any information over fake network that can easily sniff by rough server. For detail read our previous article “Comprehensive guide on sniffing”
Author: AArti Singh is a Researcher and Technical Writer at Hacking Articles an Information Security Consultant Social Media Lover and Gadgets. Contact here
Source: www.hackingarticles.in
 Reviewed by Anonymous
on
8:43 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Anonymous
on
8:43 AM
Rating: