Hackers Spotted Using Morse Code In Phishing Attacks To Evade Detection
Microsoft has disclosed details of an evasive year-long social engineering campaign wherein the operators kept changing their obfuscation and encryption mechanisms every 37 days on average, including relying on Morse code, in an attempt to cover their tracks and surreptitiously harvest user credentials.
The phishing attacks take the form of invoice-themed lures mimicking financial-related business transactions, with the emails containing an HTML file ("XLS.HTML"). The ultimate objective is to harvest usernames and passwords, which are subsequently used as an initial entry point for later infiltration attempts.
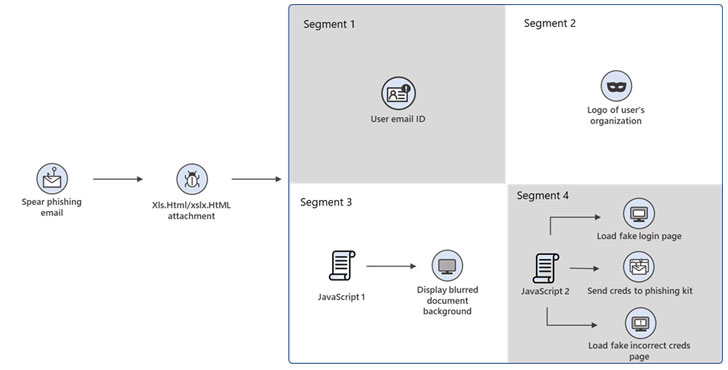
Microsoft likened the attachment to a "jigsaw puzzle," noting that individual parts of the HTML file are designed to appear innocuous and slip past endpoint security software, only to reveal its true colors when these segments are decoded and assembled together. The company did not identify the hackers behind the operation.
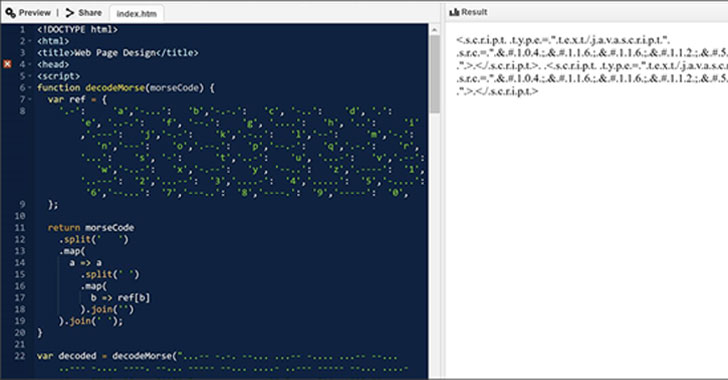
"This phishing campaign exemplifies the modern email threat: sophisticated, evasive, and relentlessly evolving," Microsoft 365 Defender Threat Intelligence Team said in an analysis. "The HTML attachment is divided into several segments, including the JavaScript files used to steal passwords, which are then encoded using various mechanisms. These attackers moved from using plaintext HTML code to employing multiple encoding techniques, including old and unusual encryption methods like Morse code, to hide these attack segments
Opening the attachment launches a browser window that displays a fake Microsoft Office 365 credentials dialog box on top of a blurred Excel document. The dialog box shows a message urging the recipients to sign in again due to reasons that their access to the Excel document has purportedly timed out. In the event the user enters the password, the individual is alerted that the typed password is incorrect, while the malware stealthily harvests the information in the background.
The campaign is said to have undergone 10 iterations since its discovery in July 2020, with the adversary periodically switching up its encoding methods to mask the malicious nature of the HTML attachment and the different attack segments contained within the file.
Microsoft said it detected the use of Morse code in the attacks' February and May 2021 waves, while later variants of the phishing kit were found to direct the victims to a legitimate Office 365 page instead of showing a fake error message once the passwords were entered.
"Email-based attacks continue to make novel attempts to bypass email security solutions," the researchers said. "In the case of this phishing campaign, these attempts include using multilayer obfuscation and encryption mechanisms for known existing file types, such as JavaScript. Multilayer obfuscation in HTML can likewise evade browser security solutions.
Source: feedproxy.google.com
 Reviewed by Anonymous
on
6:24 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Anonymous
on
6:24 AM
Rating: