Confidence In File Upload Security Is Alarmingly Low. Why?
Numerous industries—including technology, financial services, energy, healthcare, and government—are rushing to incorporate cloud-based and containerized web applications.
The benefits are undeniable; however, this shift presents new security challenges.
OPSWAT's 2023 Web Application Security report reveals:
- 75% of organizations have modernized their infrastructure this year.
- 78% have increased their security budgets.
- Yet just 2% are confident in their security posture.
Let's explore why confidence in security lags infrastructure upgrades and how OPSWAT closes that gap.
Evolving Infrastructure Outpaces Security Upgrades.
The pace of security upgrades struggles to keep up with technological advancements. This gap is especially visible in file upload security. Companies are updating their infrastructure by embracing distributed, scalable applications that leverage microservices and cloud solutions—creating new avenues of attack for criminals.
Cloud Hosting
Businesses are moving to public cloud hosting for its scalability and efficiency. Software as a Service (SaaS) sees growing adoption while private cloud and on-site hosting wane. Data is spread over multiple cloud storage providers. Unfortunately, this increases complexity and opens additional attack vectors.
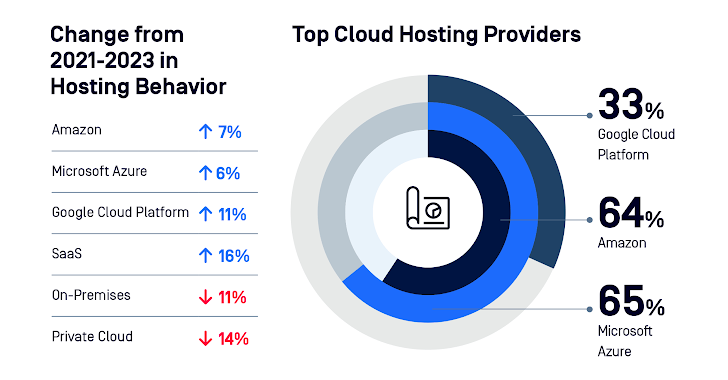 |
| Figure 1: Breakdown of cloud hosting providers |
Organizations are Shifting to Containers
97% of organizations use containers or will deploy containers over 12 months in their web hosting environments. Azure Kubernetes, AWS Kubernetes, and Docker are top choices. Misconfiguration and increased updates required for microservices open the door for file upload attacks leveraging vulnerable and outdated components.
Unsecure File Uploads Concern
Our survey highlights three primary concerns:
Data Breaches
Data breaches are the #1 concern. Reputational damage, loss in business or revenue and regulatory fines, round out the list. Cybercriminals can access sensitive data, leading to financial losses, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
Compliance
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) leads the way with the highest percentage of respondents. 56% of companies state that it was a driving factor in their security decisions.
Malware
98% of respondents are concerned about malware attacks from file uploads.
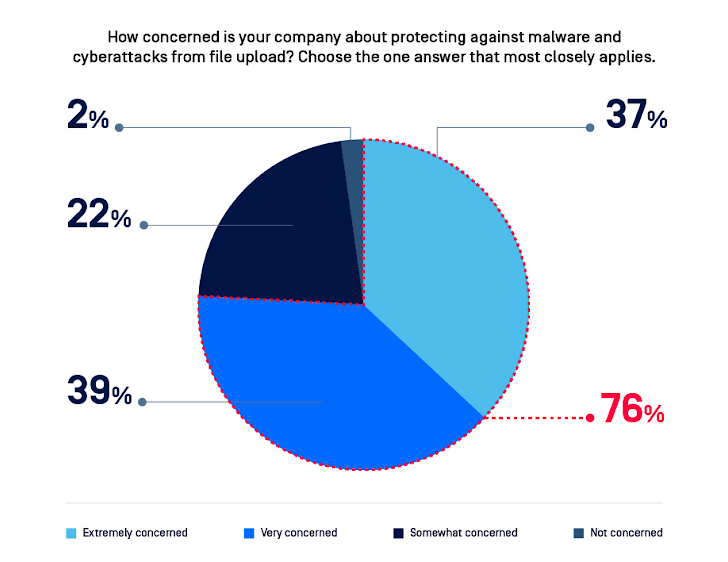 |
| Figure 2: Three quarters (76%) are "extremely" or "very concerned" about protecting against attacks. |
Click here to schedule a 15-minute demo of how OPSWAT can help secure your web applications from malicious file uploads.
File Upload Security Needs Fixing
As organizations continue to shift their operations to cloud hosting and containerized web applications, the need for effective security measures has become even more critical. This is especially true when accepting file uploads, as cybercriminals exploit file upload vulnerabilities to access secure networks.
We found that:
- Only 63% use multi-engine scans for malware.
- Just 32% disarm files via Content Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR) to tackle zero-day and embedded threats.
- Employing multiple anti-malware engines is vital. Scanning with over 30 engines hit a 99%+ accuracy rate.
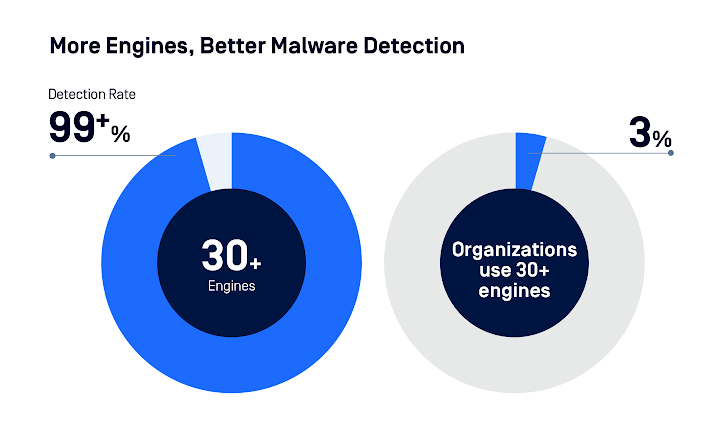 |
| Figure 3: Anti-malware scanning efficacy. |
The Path Forward
To keep pace with evolving infrastructure and increased attack surface, companies need an integrated solution utilizing prevention- and detection-based technologies.
More Antivirus Engines
Using multiple antivirus (AV) engines to secure against malicious file uploads and malware can provide additional layers of protection and increase the detection rate. Each antivirus engine has its own set of rules and algorithms for detecting a wide range of threats.
Deep CDR Disarms Active Content & Regenerates Safe Files
Our survey found that large companies remove possible threats from files with Deep CDR to disarm active content and regenerate safe files while alerting and blocking out-of-policy files with embedded objects, such as JavaScript in PDFs or macros.
 |
| Figure 4: CDR file regeneration process |
One-Billion Data Points
It's imperative to keep web applications vulnerability-free. It's highly recommended that organizations implement File-Based Vulnerability Assessment technology to detect application and file-based vulnerabilities before installation, closing any future backdoors that hackers could exploit. We use our patented technology (U.S. 9749349 B1) to assess vulnerabilities collected from over one billion data points from in-the-wild devices and users.
AI-Enabled Malware Analysis
OPSWAT Filescan performs fast adaptive threat analysis on files to detect zero-day malware and quickly find Indicators of Compromise (IOCS) from various sources, including files and URLs. It uses fuzzy hashing and similarity scores powered by machine learning to perform in-depth analysis.
Conclusion
As web application infrastructure progresses to the cloud, the attack surface grows. OPSWAT MetaDefender is the right path forward to guard against malicious file uploads and data loss. You can keep pace with the evolving threat landscape by combining key file upload security technologies that seamlessly integrate with your current infrastructure.
Ready to get a demo of our file upload security solution? Reach out to one of our security experts today.
Want more insights from the 2023 Web Application Security Report. Get it here.
Source: thehackernews.com
 Reviewed by Zion3R
on
4:39 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Zion3R
on
4:39 AM
Rating:






